Citrus 
Fresh Integration Testing
Test framework with focus on messaging applications and Microservices.
Automated integration tests with a wide range of messaging protocols and data formats!
Citrus 
Test framework with focus on messaging applications and Microservices.
Automated integration tests with a wide range of messaging protocols and data formats!
Many ready-to-use client and server components and endpoints that you can use in a test to simulate service interfaces and 3rd party applications.
→ Endpoints
Choose and combine many different message protocols HTTP REST, Kafka, JMS, TCP/IP, SOAP, FTP and many more.
→ Examples
Powerful message validators that verify message header and body content for different data formats such as XML, Json, YAML, plaintext.
→ Validators
Run Citrus with JUnit Jupiter, Quarkus, SpringBoot or Cucumber in a Maven or Gradle project.
→ Runtimes
You can choose from a set of domain specific languages to write a Citrus test in Java, XML, YAML or as a Cucumber BDD feature.
→ Domain Specific Languages
Get started with Citrus JBang and run your 1st integration test in minutes without any project setup.
→ JBang example
In a typical test scenario the system under test, for instance a Quarkus Microservices application, runs on a test infrastructure. Citrus interacts with the exposed services over various messaging transports in an automated test. Citrus is able to act both as producer and consumer during the test in order to exchange real request/response messages with the application.
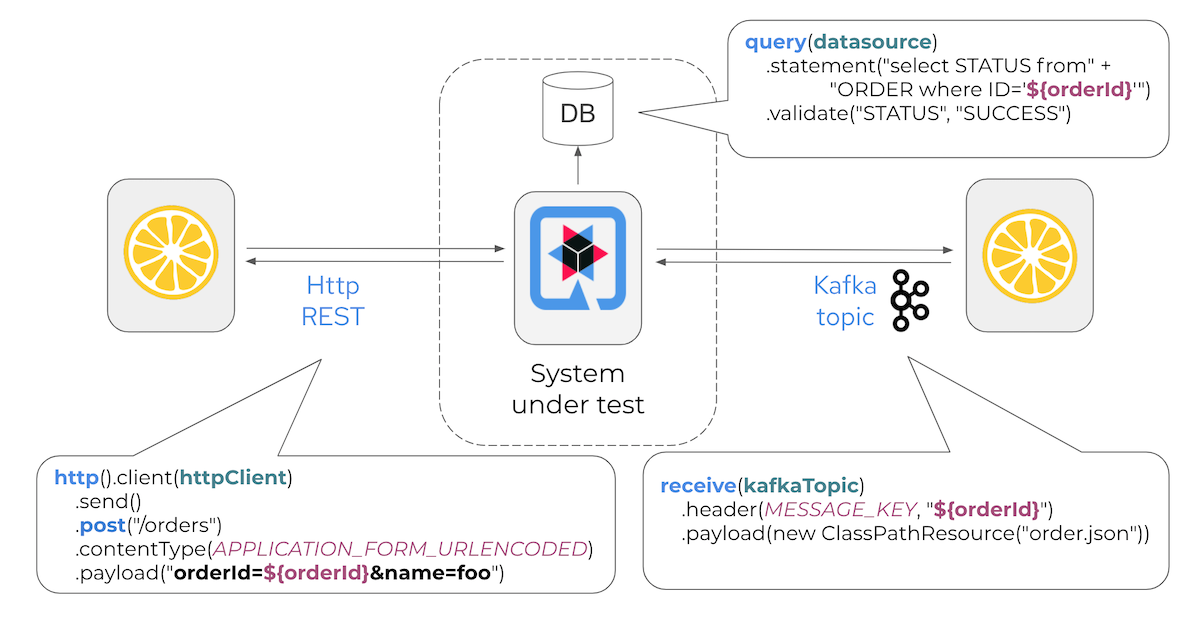
With each test step you can validate the exchanged messages with expected control data including message headers, attachments and body content (e.g. XML, Json, YAML, ...). The test provides a Java fluent API to specify the test logic and is fully automated. The repeatable test is nothing but a normal JUnit Jupiter test that can easily run as part of a Maven build or in a CI/CD pipeline.
You can easily use Citrus as part of your QuarkusTest annotated test.
→ Quarkus example
Use Citrus with Spring bean autowiring and combine Citrus with Spring Boot tests.
Citrus provides ready-to-use Cucumber steps that you can directly use in your Gherkin Given-When-Then feature files.
→ Cucumber BDD example
Manage Apache Camel routes and use one of the 300+ Camel components to exchange messages and transform data.
→ Apache Camel example
Prepare test infrastructure as part of the test using Testcontainers modules.
Easily use Selenium in Citrus to simulate user interactions in a browser.
→ Selenium example
In this podcast episode we discuss the Citrus testing framework and how it can help to verify Quarkus applications in an automated integration test.
Kamelets represent Camel K route snippets that act as standardized event sources and sinks in an event driven architecture. Kamelets provide a simple interface that hides the individual implementation details and allows the user to connect to external systems with simply providing some required properties. YAKS is a test automation tool that provides special support for Camel K, Kamelets and other technologies such as Knative, Apache Kafka, OpenAPI 3, Http REST, JMS, and many more. The presentation shows how to write automated integration tests for Kamelets with YAKS in order to run those tests as part of Kubernetes. The talk begins with a short introduction into the framework concepts and illustrates the general test automation for event sources and sinks in the form of examples and live demos. In the end the audience should be able to accomplish automated integration tests for custom Kamelets that bind to messaging technologies such as Knative, Http, and Apache Kafka.
Apache Camel K is a lightweight integration platform built from Apache Camel. Integrations built with Camel K run natively on Kubernetes and are specifically designed for serverless architectures. With the declarative nature in Camel K users can instantly run integration code written in Camel DSL on their preferred cloud. The presentation outlines typical integration scenarios with Camel K and shows how to write automated tests for these enterprise integrations. The session covers classical service provider/consumer scenarios with common messaging protocols (e.g. REST, JMS, Kafka) as well as more complex integrations with data access and 3rd party Saas services included. The tests itself will also be Cloud Native citizens and make use of Behavior Driven Development concepts.
The concept of behavior driven development (BDD) is quite simple. Business analysts and domain experts describe how the application should behave using Gherkin (given-when-then) feature stories. Developers glue those specifications to automated tests. Can we use this approach when testing the integration of services, too? The talk gives answers with a combination of the frameworks Cucumber and Citrus. After a short introduction to both frameworks we discuss the concepts and see some code examples that demonstrate how the behavior driven approach fits to testing the messaging integration with Http REST, JMS and mail communication. At the end we will have an automated integration test with BDD and almost no glue code to write manually.
The concept of behavior driven development (BDD) is quite simple. Business analysts and domain experts describe how the application should behave using Gherkin (given-when-then) feature stories. Developers glue those specifications to automated tests. The talk combines the frameworks Cucumber and Citrus and gives some code examples that demonstrate how the behavior driven approach fits to testing the messaging integration with Http REST, JMS and mail.
Citrus integrates with frameworks like Apache Camel, Arquillian, Kubernetes and Docker in order to provide automated integration testing of Microservice applications. The tools in action session gives a brief introduction to the Citrus framework and shows code samples for a complete integration test scenario in a Microservices environment.
Citrus is Open Source!
Please get involved and help!
Add comments, open new issues or pull requests with your changes on the
Citrus code repository